Which laptop processor is the best? What should you look for? What’s right for you? Why does one and the same processor have a different name? These are the questions everyone who wants to buy a laptop asks themselves.
We often make decisions about buying a laptop, taking into account what kind of processor it uses. In this case, it is important not to make a mistake. For some, choosing the right processor for a laptop is not that easy. The problem is that there have been huge changes in this issue in recent years, so some people don’t have a full understanding of the topic and may feel confused and confused. Our guide will help you better understand the differences between different laptop processors and make an informed decision.
I will also give you a laptop processor comparison so that you can clearly choose the best processor for your laptop.
Intel or AMD in a laptop?
Just like in desktops, we can distinguish two main processor manufacturers in laptops: Intel and AMD. Therefore, at the beginning of the process of buying a new laptop, the following question may arise: choose a model with an AMD processor or with an Intel processor?
Until recently, the choice was easy, because Intel dominated the segment of mobile devices, and most available models were based on this platform. In recent years, however, the situation has changed, because new AMD processors have appeared on the market. They are much better than their predecessors, so they can confidently compete with Intel models.
The effect is that there are interesting laptop configurations available on the platforms of both manufacturers, so you can’t say that you can only count on Intel products or only AMD. Both companies offer processors from different segments. All the more interesting and useful for us, the consumers. So let’s try to get to the bottom of this issue.
See also: AMD vs. Intel.
Intel processors in laptops
Quite often I am asked for advice when choosing a laptop. You begin to tell, and the interlocutor asks to explain, what all these letters and figures in the marking of processors mean.
Now I will try to explain on this picture how to decipher the names of Intel processors. To do that I will split the name of one processor into several segments:

As you can see, everything is quite simple, so I will not go into the nuances. Later we will look at the differences between the different processor series. It is better to understand what kind of processor is used for what type of laptop. Here we can list a few processor segments:
- Celeron Nxxxxx / Pentium Silver Nxxxxx (e.g. Pentium Silver N5000) – basic models for cheap laptops;
- Core iX-xxxxU (e.g. Core i7-10510U) – low-voltage processors for home laptops and ultrabooks in the business segment;
- Core iX-xxxxxY (e.g. Core i7-8500Y) – low-voltage models for the smallest laptops and ultrabooks (often with passive cooling)
- Core iX-xxxxxGx (e.g. Core i7-1065G7) – low-voltage models, where the number after the letter G stands for integrated graphics cores;
- Core iX-xxxxH / HK (e.g. Core i5-10300H) – efficient processors for mobile workstations and gaming notebooks – in fact, they are desktop processor models;
- Xeon W-xxxxM (e.g. Xeon W-10885M) – efficient processors for mobile workstations (professional equivalents of Core iX-xxxxH models).
Intel® Core™ Processor Suffixes
To understand what a processor suffix indicates, consult the list below. Not all processor generations or families include all product suffixes.
| Suffix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| G1-G7 | Graphics level (processors with new integrated graphics technology only) |
| E | Embedded |
| F | Requires discrete graphics |
| G | Includes discrete graphics on package |
| H | High performance optimized for mobile |
| HK | High performance optimized for mobile, unlocked |
| HQ | High performance optimized for mobile, quad core |
| K | Unlocked |
| S | Special edition |
| T | Power-optimized lifestyle |
| U | Mobile power efficient |
| Y | Mobile extremely low power |
| X/XE | Unlocked, High End |
| B | Ball Grid Array (BGA) |
I’m sure that this information is enough to understand which processor is offered to you in this or that laptop. You can read more about understanding the code of Intel processor models on their official website.
Read also: Best Laptop Brand in the World
AMD processors in laptops
The situation is similar for AMD processors, if you know how to read the specifications of the company’s products.
In practice, we are dealing with several processor segments:
- Seria A – obsolete processors used in the cheapest laptops to run simple programs;
- Athlon / Athlon Silver xxxxU (e.g. AMD Athlon Silver 3050U) – low voltage processors for cheap laptops;
- Ryzen x xxxxU (e.g. Ryzen 5 4500U) – low-voltage models for home and business laptops;
- Ryzen x Pro xxxxU (e.g. Ryzen 7 Pro 4750U) – low-voltage models with additional extensions for business laptops;
- Ryzen x xxxxH / HS (e.g. Ryzen 7 4600H) – efficient processors for mobile workstations and gaming laptops.
On the official AMD website you can read the transcripts of their processor codes.
Laptop processors ranking
What is the best processor for a laptop? When choosing a laptop, we are faced with dozens of processors in several different segments, so less experienced buyers may feel confused. But there is a way to determine the best processor! Both manufacturers use similar labeling systems that make it easy to determine the positioning of the units. Just look at the series, generation and model of the processor (but it has to be a model from the same segment and generation). It should be noted that sometimes the new generation can be much better than the previous one.
In the case of Intel, processors from the weakest to the most efficient can be classified like this:
- Celeron
- Pentium/Pentium Silver
- Core i3
- Core i5
- Core i7
- Core i9
The following breakdown was used for AMD models:
- Athlon/Athlon Silver
- Ryzen 3
- Ryzen 5
- Ryzen 7
- Ryzen 9
For example, if you are wondering which processor to choose for your laptop – i5 or i7 – you will immediately know that the Core i7 model will be more productive than the Core i5. However, it is worth carefully checking the specifications of comparable systems, because the difference in specifications may not be significant (for example, the number of cores will be the same, but the clock frequencies will be different), but it will have a significant impact on the price of the laptop.
Read also: Best Laptop for Programming and Coding
Processor types on laptops
What does the choice of processor look like in practice? We can actually list the three most popular laptop segments due to the processors used.
Here we have to remember first of all the basic models. So we start with models that do not have high parameters, but are very cheap. An additional advantage is the low power consumption, which means a long life. As far as Intel is concerned, these are the Celeron and Pentium Silver series, and in the case of AMD, the Athlon series.
The Intel Celeron / Pentium and AMD Athlon models have proven themselves in laptops for the most basic tasks – such as surfing the Internet, watching movies, or general office work. They are cheap configurations for home or school, and you should not expect good performance, but they do their job.
The second category is even more interesting. These are the so-called low voltage processor models. They are the most common processors in modern laptops (they are distinguished by U or Y markings – for example, Intel Core i5-10210U or AMD Ryzen 5 4500U). These processors use more efficient cores, but the specification forces them to reduce the supply voltage and clock frequency. Such systems are also characterized by lower power consumption and, as a consequence, allow to have longer battery life, do not produce a lot of heat and can be used in thinner designs. However, reduced clock speeds result in weaker performance than standard models that are labeled H.
Low-voltage processors are suitable for home laptops to use for basic software compact designs for business users. This is a good suggestion for situations where you need to find the right compromise between performance, battery life and case size.
The third category is the most interesting for users. We are talking about efficient notebook processors. These models can be identified with the H marking (e.g. Intel Core i7-10750H or AMD Ryzen 7 4800H). Laptop configurations with these processors offer better performance than models with low-voltage versions. However, high performance means more power consumption, more heat produced, so it requires a more efficient cooling system. Often it also has the effect of reducing the operating time of the built-in battery.
Models from the H-segment will perform well in programs where good performance is a priority. These are primarily gaming notebooks and mobile workstations for content creation, film and video editing for YouTube, graphics editing and 3D design.
See also: Best Ultrabook Under $1000
What’s the difference between a laptop processor and a computer processor?
Finally, a few more tips that can help you choose the right processor.
First of all, we are talking about the parameters of the systems themselves. Laptop processors should at least have lower power consumption, so they offer worse specs than desktop devices. So we won’t find as many cores here, and they won’t run at such high clock speeds. Parameters affect performance, so laptop processors usually offer lower performance than desktop processors (assuming we’re comparing models from similar segments and the same generation). But the compactness and convenience of laptops offset this advantage.
It is worth noting, however, that in recent years we have seen significant technological advances allowing for sophisticated and more efficient notebook processors. An example? Not long ago, 6-core and 8-core processors were reserved for efficient PCs, and lately they are not something strange and unusual for laptops (and even compact ones).
Laptop Processors Ranking by Relative Performance
I have no doubt that many people are asking a more straightforward question: what is the most powerful laptop processor? The charts below provide the answer to that question.
| AMD Ryzen 9 5900HX | 100% |
| Intel Core i9-11980HK | 99.9% |
| Intel Core i9-11950H | 98% |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5980HS | 97.1% |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5900HS | 96% |
| Intel Core i9-11900H | 94.7% |
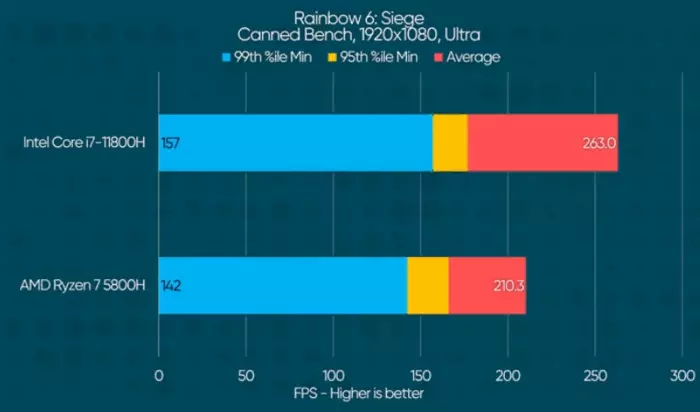
| Intel Core i7-11850H | 92.7% |
| Intel Core i7-11800H | 92.2% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800H | 92.2% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800HS | 89.4% |
| AMD Ryzen 9 4900HS | 83.4% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800U | 82.5% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 4800H | 81.6% |
| AMD Ryzen 9 4900H | 80.8% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 4800HS | 80.7% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 Extreme Edition | 77.4% |
| Intel Core i5-11500H | 74.6% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600H | 74.2% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 4800U | 73.4% |
| Intel Core i9-10980HK | 70.6% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5700U | 70.1% |
| Intel Core i7-10700TE | 69.5% |
| Intel Core i9-10885H | 67.8% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600U | 67.5% |
| Intel Core i5-11400H | 67.2% |
| Intel Core i7-10875H | 66.4% |
| Intel Core i9-10880H | 65.5% |
| Intel Core i7-10870H | 65.5% |
| Apple M1 | 64.5% |
| Intel Core i9-9980HK | 63.7% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 4600H | 63% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 4600HS | 62.5% |
| Intel Core i7-1195G7 | 60.4% |
| Intel Core i5-11260H | 60.2% |
| Intel Core i9-9880H | 60% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 4700U | 58.5% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 4600U | 58.3% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5500U | 56.6% |
| Intel Core i7-10750H | 53.3% |
| Intel Core i7-11370H | 52.8% |
| Intel Core i7-11375H | 52.8% |
| Intel Core i5-10500H | 52% |
| Intel Core i7-10850H | 51.7% |
| AMD Ryzen 3 5400U | 51.6% |
| Intel Core i7-1185G7E | 49.6% |
| Intel Core i7-9750HF | 49.3% |
| Intel Core i7-9850H | 49.3% |
| Intel Core i5-11300H | 48.5% |
| Intel Core i7-9750H | 48% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 4500U | 47.8% |
| Intel Core i7-1160G7 | 46.8% |
| Intel Core i7-1185G7 | 46.5% |
| Intel Core i5-1145G7 | 45.9% |
| Intel Core i7-9700TE | 45.6% |
| Intel Core i7-1165G7 | 45.4% |
| Intel Core i5-1130G7 | 44.8% |
| Intel Core i7-1068NG7 | 44.1% |
| Intel Core i5-1135G7 | 43.1% |
| AMD Ryzen 3 5300U | 43% |
| Intel Core i7-10710U | 42.9% |
| Intel Core i3-1125G4 | 42.8% |
| Intel Core i5-1038NG7 | 41.6% |
| Intel Core i5-9400F | 40.6% |
| Intel Core i5-9500TE | 39.2% |
| Intel Core i7-9850HL | 38.8% |
| Intel Core i5-10400H | 38% |
| Intel Core i7-1065G7 | 37.5% |
| Intel Core i7-10810U | 37.4% |
| Intel Core i5-10300H | 37.3% |
| Intel Core i5-10200H | 36% |
| Intel Core i5-1035G7 | 35.8% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3750H | 35.5% |
| Intel Core i5-1035G4 | 35.3% |
| Intel Core i5-9400H | 35.2% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3550H | 34.4% |
| AMD Ryzen 3 4300U | 34.3% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3500U | 33.7% |
| Intel Core i5-1035G1 | 33.4% |
| Intel Core i5-9300H | 33.4% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3580U | 33.2% |
| Intel Core i5-9300HF | 32.6% |
| Intel Core i3-10100T | 31.7% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3780U | 31.4% |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3700U | 31.3% |
| Intel Core i7-1060NG7 | 31.2% |
| Intel Core i7-10610U | 30.3% |
| Intel Core i7-5850EQ | 30% |
| Intel Core i7-10510U | 29.3% |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3450U | 29% |
| Intel Core i5-10210U | 28.7% |
| Intel Core i5-10310U | 28.5% |
| Intel Core i3-1115G4 | 27.5% |
| Intel Core i5-1030NG7 | 26.6% |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3300U | 24.9% |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3350U | 24.9% |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 23.1% |
| Intel Core i7-10510Y | 22.5% |
| Intel Core i3-1005G1 | 22.4% |
| Intel Core i5-10210Y | 20.6% |
| Intel Pentium 6805 | 20.2% |
| AMD Athlon Silver 3050GE | 19.4% |
| Intel Core i3-9100TE | 19.2% |
| AMD Athlon Gold 3150U | 18.7% |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3250U | 17.5% |
| Intel Core i3-10110U | 17.3% |
| Intel Core i3-1000NG4 | 17.3% |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3200U | 16.8% |
| Intel Core i3-10110Y | 14.7% |
| Intel Core i5-L16G7 | 14.6% |
| Intel Pentium Silver N5030 | 11.3% |
| Intel Celeron N5100 | 11.2% |
| Intel Pentium 6405U | 10.1% |
| Intel Core i3-6102E | 10% |
| Intel Pentium 5405U | 9.7% |
| Intel Celeron 6305 | 9.6% |
| Intel Pentium 4417U | 9.5% |
| Intel Celeron 4305UE | 8.3% |
| Intel Pentium 4425Y | 7.2% |
| Intel Celeron 5205U | 5.8% |
Is it possible to replace the processor in a laptop?
The other difference tends to lie on the practical side of this comparison. We know that desktop processors are installed in a socket (a special connector on the motherboard), so you can mount them yourself, and if necessary, after some time there is even an opportunity to replace the processor with a better one. As for modern laptops, the situation is quite different, because the chips are pre-soldered to the motherboard. So this solution prevents replacement / upgrade, but allows you to build a thinner device. This means that it is almost impossible to replace the processor in a laptop at home. In addition, not every service center will do it either. Although there may be exceptions.
An exception may also be some gaming laptops and mobile workstations, where manufacturers use more efficient processors for desktops. However, such configurations are quite rare. In addition, the price of such solutions is almost exorbitant.
See also: Most Durable and Reliable Laptop
Is it possible to speed up the processor in a laptop?
Some of you are probably wondering if it is possible to overclock the processor in a laptop. So, some models can indeed be configured, that is, overclocked. Here it should be noted that currently this feature is offered only by Intel chips with an unlocked multiplier (like models for desktops, they are marked with a K – for example, Core i9-10980HK). By the way, they are quite rare, although you can find laptops with such processors.
How to overclock the processor in a laptop? This procedure is very similar to overclocking the processor on a computer. First of all, here you can use the Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU). If you are interested in the details, there are many articles about overclocking. I’m sure you can find them yourself if you want to.
Another thing is whether it is worth overclocking the processor in your laptop. You need to understand that then we get better performance, but at the same time increase the amount of heat produced (which can lead to throttling the processor), will increase power consumption, as well as such a process reduces battery life. Therefore, it is worth considering whether it is necessary to overclock the processor in a laptop. The effect of this will be minimal, but will add problems.
What processors for laptops we recommend in 2024
Choosing a laptop processor is not as difficult a task as it may seem at first. You should start by determining the purpose of your laptop and choosing the appropriate processor for it. Of course, you should not expect miracles here, because each segment has its own strengths and weaknesses. If you are planning to buy a cheap laptop with a powerful processor that will provide long battery life, it is almost unrealistic.
So, which laptop processor to choose for 2024? Recently we have seen significant technical progress, so we advise to choose models of the latest generations. The fact is that they are often characterized by greater efficiency and also offer better functionality. So here are tips for the best solutions today:
- Inexpensive home laptop: Intel Core 10xxxU or AMD Ryzen 4xxxU
- Work laptop: Intel Core 10xxxU or AMD Ryzen 4xxxU
- gaming or content production: Intel Core 10xxxH or AMD Ryzen 4xxxH.
Conclusion
It’s worth noting, however, that in real life we don’t really choose a laptop processor, but a laptop with a specific processor. The same CPU is often found in many different models, from different manufacturers, and they may differ in design, such as cooling system and other components. Differences can affect the performance of the CPU and without thorough testing, the impact will be difficult to determine.


![Laptop Battle of [year]: Lenovo vs. Dell vs. HP](https://whattdw.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/1-18.webp)





